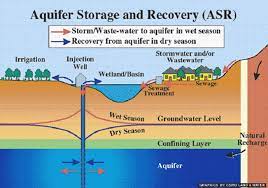
Urban and peri-urban areas in the Philippines and other developing regions face increasing flood risks due to climate change, rapid urbanization, and impermeable infrastructure. These floods pose serious threats to human life, health, property, and economic activity. Simultaneously, groundwater aquifers are being depleted due to reduced infiltration caused by paved surfaces and disrupted natural hydrological cycles.
Flood control in the Philippines has long been dominated by expensive, temporary engineering projects that fail under the weight of prolonged rains. By contrast, groundwater aquifer recharge offers a permanent, sustainable, and multi-benefit solution.
This is not only flood control—it is water security, environmental restoration, and climate resilience combined.
|
Integrating flood control with groundwater recharge aquifers, offering benefits that go beyond conventional drainage and pumping systems:
1) Prevents Urban Flooding – Rapid injection prevents water buildup in city centers, ensuring drainage systems remain effective.
2) Maintains Safe River Levels – Diverts excess floodwater into aquifers, reducing overflow and backflow risks.
3) Provides Alternative Water Supply – Recharged aquifers serve as a reliable source during droughts.
4) Supports the Natural Water Cycle – Restores hydrological balance to sustain ecosystems and biodiversity.
5) Prevents Land Degradation – Reduces risks of sinkholes, subsidence, and erosion by replenishing groundwater.
6) Builds Climate Resilience – A dual solution for both flooding and drought, adaptable to extreme weather.
|

|
| |
OBJECTIVE
To mitigate urban flooding in urban communities by designing and implementing a flood control system that captures peak runoff during storm events and continuously discharges excess water into the underlying groundwater aquifer. This system aims to stabilize surface water levels, prevent flood height escalation, and enhance aquifer recharge for long-term water resilience.
Strategic Goal
Reduce peak flood discharge from upland catchments and prevent downstream river overflow by intercepting, detaining, and infiltrating runoff before it reaches low-lying urban basins. |
| |
The integrated flood control and recharge system comprises three primary components:
1. Detention Basin
2. Pumping System
3. Borewell Groundwater Recharge Assembly
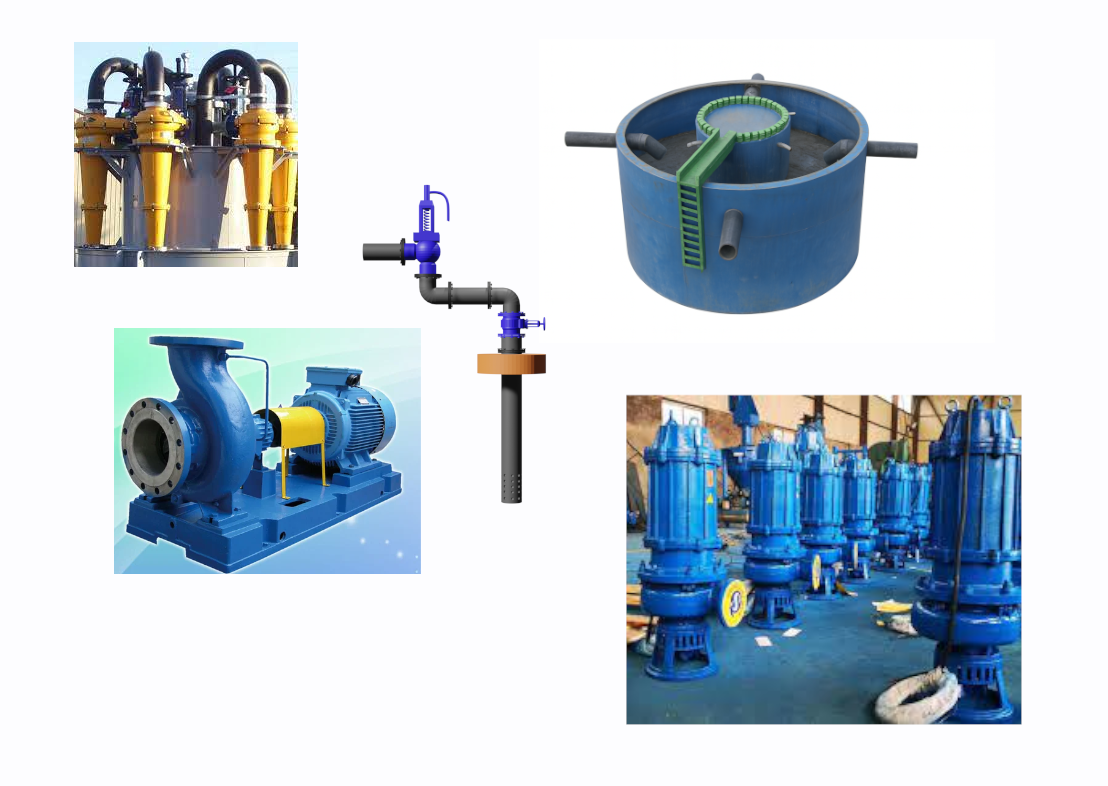

1. Flood Detention Basin
• A strategically located basin designed to collect excess surface runoff during heavy rainfall events.
• Constructed from reinforced concrete with sediment traps and overflow channels to prevent urban flooding.
• Structure: o Outer circular wall: Contains multiple inlet pipes for incoming floodwater.
2. Hydrocyclone Separator
• A mechanical separator that removes suspended solids and debris from collected water using centrifugal force.
• Ensures only clean water proceeds to the injection system, reducing clogging and contamination risk.
• Filtration efficiency: 40–100 microns, ensuring safe quality for aquifer recharge.
• Operation: A submersible pump feeds water under high pressure to the hydrocyclone inlet, initiating centrifugal separation.
3. Injection (High-Pressure) Water Pump
• A high-pressure centrifugal pump that transfers filtered water from the separator to the borewell system for deep aquifer injection.
• Equipped with flow control valves, pressure gauges, and a backflow prevention system to regulate injection rates and ensure safe operation.
4. Borewell Pipe
• A vertical pipe assembly designed for deep subsurface water injection.
• Perforated sections and gravel packing enhance infiltration and prevent backflow. |
| |
FLOW PROCESS
Flood Control Process Flow: Absorb and Discharge The system operates on an absorb-and-discharge principle. Floodwater from the catchment area is directed toward a flood control detention basin, where it undergoes temporary storage and treatment. From there, the water is Simultaneously discharged downstream into the groundwater aquifer.
This mechanism captures peak runoff during storm events, regulates discharge rates, and prevents the escalation of flood heights. By allowing controlled infiltration into the aquifer, the system helps stabilize surface water levels, reduce flood risks, and enhance groundwater recharge, strengthening long-term water resilience in the region. |
| |

|
| |
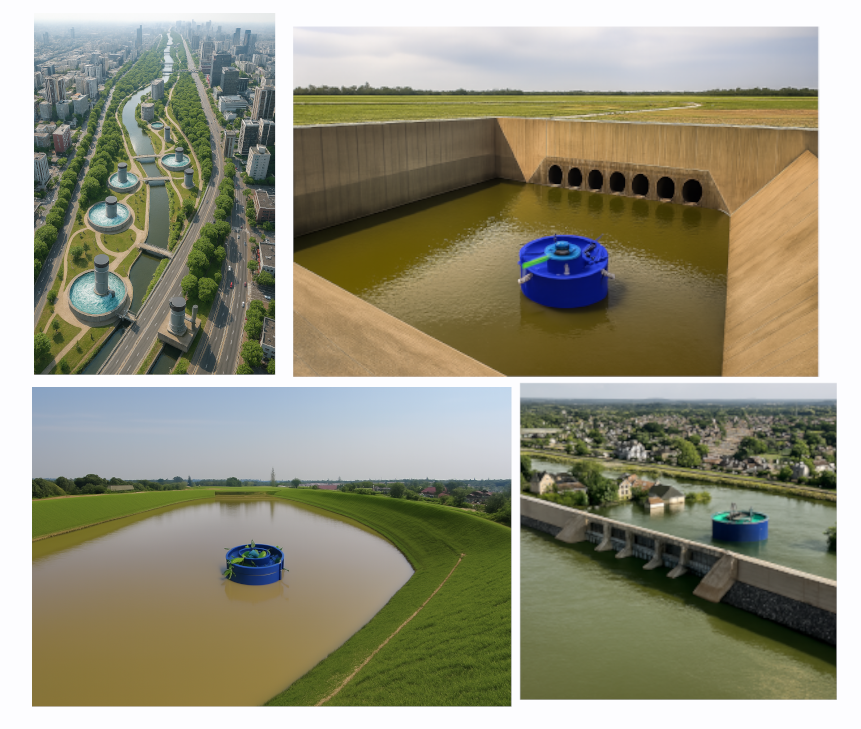
Multi-Allocated Flood Control System in Sub-Catchment Basins
A multi-allocated flood control system within the sub-catchment basins is designed to absorb and discharge stormwater runoff directly into the groundwater aquifer. By distributing flood control across multiple sub-catchments, the system reduces the runoff load on the main river stream, minimizing flood peaks and improving overall hydrological balance. This decentralized approach enhances infiltration capacity, supports aquifer recharge, and ensures more |

|
Recovery / Harvesting Groundwater Aquifer in multi location
The recharged aquifer creates an abundant reserve of groundwater, which can later be harvested from various upstream recovery sites to support water supply needs, sustain ecosystems, and improve long-term water security and resilience. |
| |


|
| |